TI-BASIC:R Pr
From Learn @ Cemetech
Jump to navigationJump to search
Command Summary
R►Pr( calculates the radius component (in polar coordinates) given the Cartesian coordinates.
Command Syntax
R►Pr(x,y)
Menu Location
Press:
- 2nd ANGLE to access the angle menu.
- 5 to select R►Pr(, or use arrows and ENTER.
TI-83/84/+/SE
1 byte
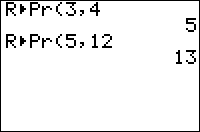
R►Pr( (Rectangular to polar radius) takes the (x,y) (Cartesian) coordinates, and gives the radius coordinate r of the same point in (r,θ) (polar) mode. The identity used for this conversion is r² = x²+y²
R►Pr(3,4)
5
√(3²+4²)
5
R►Pr({6,5},{8,12})
{10 13}
The function works even when the equivalent √(x²+y²) fails due to overflow:
R►Pr(3e99,4e99) 5e99
Optimization
R►Pr( is the smallest way to implement the distance formula <math>d=\sqrt{(x_1-x_2)^2+(y_1-y_2)^2}</math>. Just pass it the values x,,1,,-x,,2,, and y,,1,, - y,,2,, as arguments:
:√((5-2)²+(4-0)²) can be :R►Pr(5-2,4-0)
Error Conditions
- ERR:DATA TYPE is thrown if you input a complex argument.
- ERR:DIM MISMATCH is thrown if two list arguments have different dimensions.