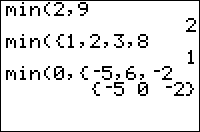TI-BASIC:Min
Command Summary
Returns the minimum of two elements or of a list.
Command Syntax
- for two numbers: min(x,y)
- for a list: min(list)
- comparing a number to each element of a list: min(x,list) or min(list,x)
- pairwise comparing two lists: min(list1,list2)
Menu Location
Press:
- MATH to access the Math menu.
- RIGHT to access the NUM submenu.
- 6 to select min(, or use arrows.
Alternatively, press:
- 2nd LIST to access the list menu.
- LEFT to access the MATH submenu.
- ENTER to select min(.
TI-83/84/+/SE
1 byte
min(x,y) returns the smallest of the two numbers x and y. min(list) returns the smallest element of list. min(list1,list2) returns the pairwise minima of the two lists. min(list1,x) (equivalently, min(x,list1)) returns a list whose elements are the smaller of x or the corresponding element of the original list.
min(2,3)
2
min({2,3,4})
2
min({1,3},{4,2})
{1 2}
min({1,3},2)
{1 2}
Unlike relational operators, such as < and >, min( can also compare complex numbers. To do this, both arguments must be complex -- either complex numbers or complex lists: min(2,i) will throw a ERR:DATA TYPE error even though min(2+0i,i) won't. In the case of complex numbers, the number with the smallest absolute value will be returned. When the two numbers have the same absolute value, the second one will be returned: min(i,-i) returns -i and min(-i,i) returns i.
Advanced Uses
min( can be used in Boolean comparisons to see if every value of a list is 1 (true) -- useful because commands like If or While only deal with numbers, and not Lists, but comparisons like L1=L2 return a list of values. In general, the behavior you want varies, and you will use the min( or Max( functions accordingly.
Using min( will give you a strict test -- only if every single value of a list is true will min( return true. For example, the following code will test if two lists are identical -- they have the same exact elements -- and print EQUAL in that case:
:If dim(L1)=dim(L2 :Then :If min(L1=L2 :Disp "EQUAL :End
The first check, to see if the sizes are identical, is necessary because otherwise comparing the lists will return a ERR:DIM MISMATCH error.
Error Conditions
- ERR:DATA TYPE is thrown when comparing a real and a complex number. This can be avoided by adding 0i to the real number.
- ERR:DIM MISMATCH is thrown, when using min( with two lists, if they have different dimensions.