TI-BASIC:Cos: Difference between revisions
Initial automated import |
Automated superscript correction |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
= Advanced Uses = | = Advanced Uses = | ||
You can bypass the mode setting by using the [[TI-BASIC:Degree_Symbol|°]] (degree) and | You can bypass the mode setting by using the [[TI-BASIC:Degree_Symbol|°]] (degree) and <sup>[[TI-BASIC:Radian_Symbol|r]]</sup> (radian) symbols. These next two commands will return the same values no matter if your calculator is in degrees or radians: | ||
cos(60°) | cos(60°) | ||
Latest revision as of 22:23, 24 February 2016
Command Summary
Returns the cosine of a real number.
Command Syntax
cos(angle)
Menu Location
Press [COS]
TI-83/84/+/SE
1 byte
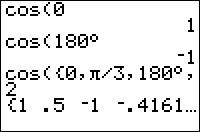
cos(θ) returns the cosine of θ, which is defined as the x-value of the point of intersection of the unit circle and a line containing the origin that makes an angle θ with the positive x-axis
The value returned depends on whether the calculator is in Radian or Degree mode. A full rotation around a circle is 2π radians, which is equal to 360°. The conversion from radians to degrees is angle*180/π and from degrees to radians is angle*π/180. The cos( command also works on a list of real numbers.
In radians:
cos(π/3)
.5
In degrees:
cos(60)
.5
Advanced Uses
You can bypass the mode setting by using the ° (degree) and r (radian) symbols. These next two commands will return the same values no matter if your calculator is in degrees or radians:
cos(60°)
.5
cos(π/3^r)
.5
Error Conditions
- ERR:DATA TYPE is thrown if you supply a matrix or a complex argument.
- ERR:ARGUMENT is thrown if you use more than one number.