TI-BASIC:Radian Symbol: Difference between revisions
Initial automated import |
Automated superscript correction |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:TI-BASIC:Command | {{Template:TI-BASIC:Command | ||
|picture=RADIAN.GIF | |picture=RADIAN.GIF | ||
|summary=If the calculator is in degree mode, the | |summary=If the calculator is in degree mode, the <sup>r</sup> (radian) symbol converts a radian angle to degrees. | ||
|syntax=''angle'' | |syntax=''angle''<sup>r</sup> | ||
|location=Press: | |location=Press: | ||
# 2nd ANGLE to access the angle menu. | # 2nd ANGLE to access the angle menu. | ||
# 3 to select | # 3 to select <sup>r</sup>, or use arrows and ENTER. | ||
|compatibility=TI-83/84/+/SE | |compatibility=TI-83/84/+/SE | ||
|size=1 byte | |size=1 byte | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Template:TI-BASIC:Markup cmd= | {{Template:TI-BASIC:Markup cmd=<sup>r</sup>}} | ||
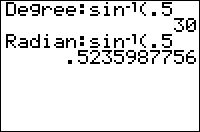
Normally, when the calculator is in degree mode, the trigonometric functions only return values calculated in degrees. With the | Normally, when the calculator is in degree mode, the trigonometric functions only return values calculated in degrees. With the <sup>r</sup> symbol you can have the angle evaluated as if in radian mode because it converts the angle into degrees. | ||
One full rotation around a circle is 2π radians, which is equal to 360°. To convert an angle in radians to degrees you multiply by 180/π, and to convert from degrees to radians multiply by π/180. | One full rotation around a circle is 2π radians, which is equal to 360°. To convert an angle in radians to degrees you multiply by 180/π, and to convert from degrees to radians multiply by π/180. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:26, 24 February 2016
Command Summary
If the calculator is in degree mode, the r (radian) symbol converts a radian angle to degrees.
Command Syntax
angler
Menu Location
Press:
- 2nd ANGLE to access the angle menu.
- 3 to select r, or use arrows and ENTER.
TI-83/84/+/SE
1 byte
{{Template:TI-BASIC:Markup cmd=r}}
Normally, when the calculator is in degree mode, the trigonometric functions only return values calculated in degrees. With the r symbol you can have the angle evaluated as if in radian mode because it converts the angle into degrees.
One full rotation around a circle is 2π radians, which is equal to 360°. To convert an angle in radians to degrees you multiply by 180/π, and to convert from degrees to radians multiply by π/180.
In degree mode:
sin(π) \\sine of Pi degrees .0548036651 sin(π^^r) 0
In radian mode:
sin(π) 0 sin(π^^r) 0 \\There's no difference when in radians
Optimization
When you only call the trig function once in a program and want it calculated in radians, instead of changing the mode you can just use ° to save one-byte (the newline from using the command Radian)
:Radian :sin(X) can be :sin(X^^r)
Related Commands
- ° (degree symbol)